
Potential energy due to or stored in electric fields The sum of macroscopic translational and rotational kinetic and potential energies Some forms of energy (that an object or system can have as a measurable property)
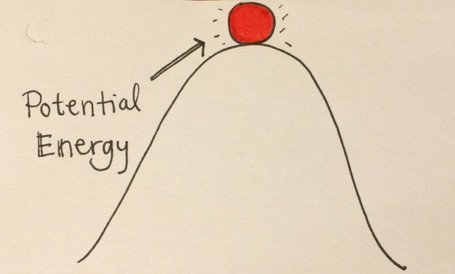
For example, the sum of translational and rotational kinetic and potential energy within a system is referred to as mechanical energy, whereas nuclear energy refers to the combined potentials within an atomic nucleus from either the nuclear force or the weak force, among other examples. While these two categories are sufficient to describe all forms of energy, it is often convenient to refer to particular combinations of potential and kinetic energy as its own form. Kinetic energy is determined by the movement of an object – or the composite motion of the components of an object – and potential energy reflects the potential of an object to have motion, and generally is a function of the position of an object within a field or may be stored in the field itself. The total energy of a system can be subdivided and classified into potential energy, kinetic energy, or combinations of the two in various ways.

Thermal energy is energy of microscopic constituents of matter, which may include both kinetic and potential energy. In a typical lightning strike, 500 megajoules of electric potential energy is converted into the same amount of energy in other forms, mostly light energy, sound energy and thermal energy. ( September 2016) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message) Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. This section needs additional citations for verification. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven by the energy the planet receives from the Sun (although a small amount is also contributed by geothermal energy). Human civilization requires energy to function, which it gets from energy resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear fuel, or renewable energy. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy.ĭue to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass when stationary (called rest mass) also has an equivalent amount of energy whose form is called rest energy, and any additional energy (of any form) acquired by the object above that rest energy will increase the object's total mass just as it increases its total energy. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).Ĭommon forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system.
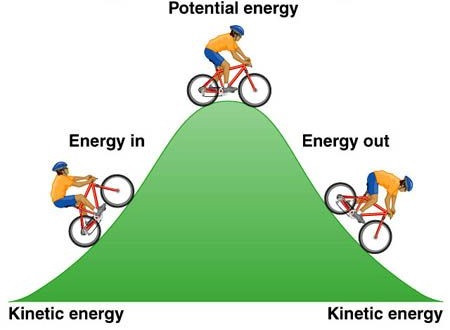
Energy is a conserved quantity-the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια ( enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
